LED headlight bulbs have emerge as increasingly more famous within the automobile enterprise because of their numerous advantages together with electricity efficiency, durability, and advanced brightness. One key feature that units LED headlights other than conventional halogen bulbs is the presence of an connected radiator. But why do LED headlight bulbs require radiators? Let's delve into the motives at the back of this crucial element.
LEDs are renowned for his or her ability to supply shiny and severe light while eating appreciably much less electricity in comparison to halogen bulbs. However, the manner of converting electrical strength into light produces warmth as a byproduct. Since excessive warmness can adversely have an effect on the overall performance and durability of the LEDs, it turns into essential to deplete this heat successfully. Enter the radiator.
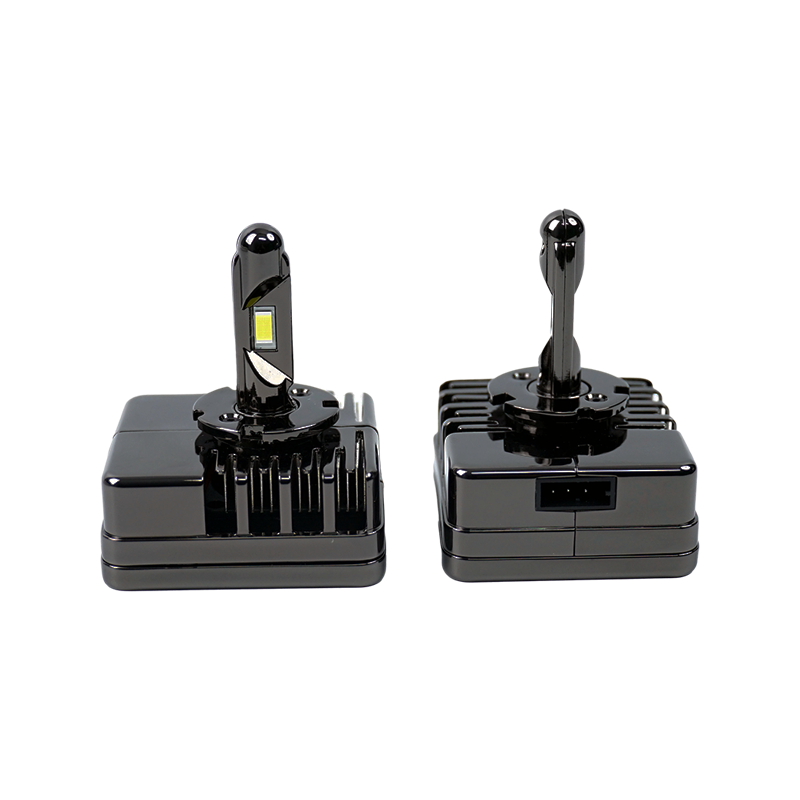
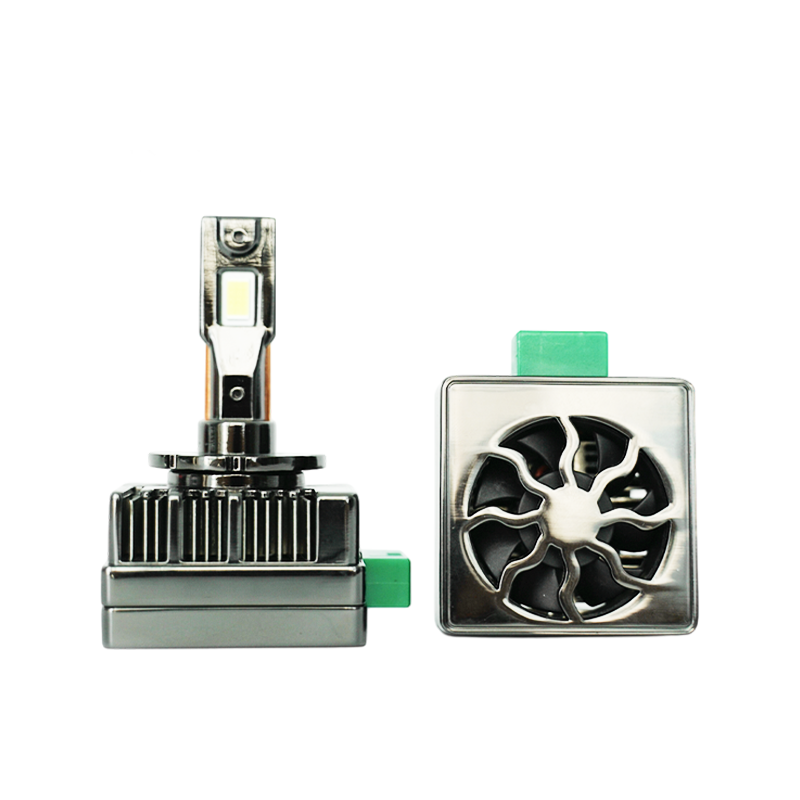
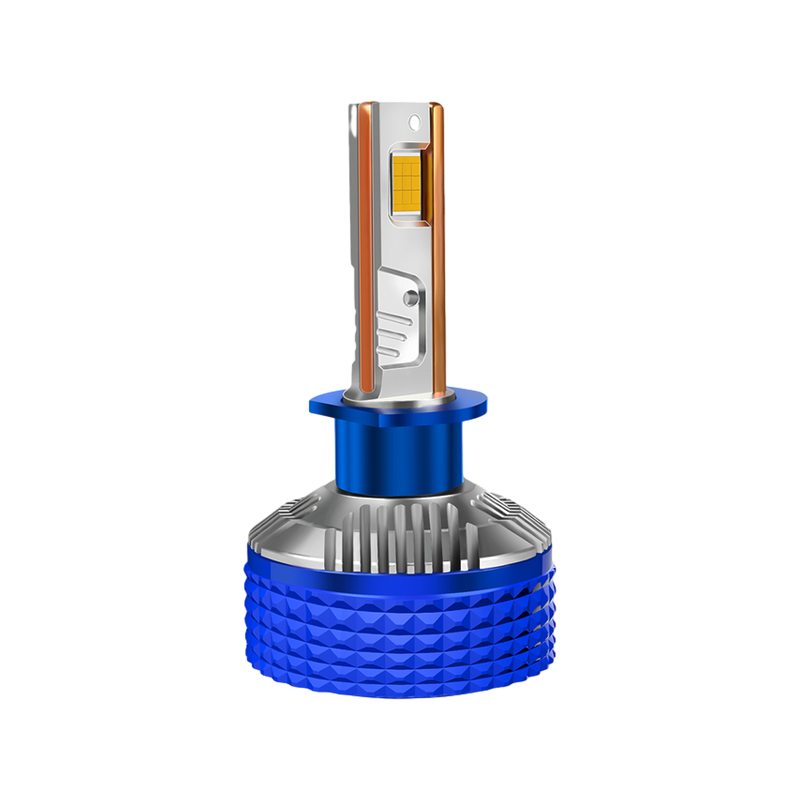
A radiator, inside the context of LED headlight bulbs, refers to a heat sink or a cooling machine designed to dissipate the excess warmness generated in the course of operation. It facilitates keep a appropriate working temperature for the LEDs, making sure their optimum functionality and extended lifespan.
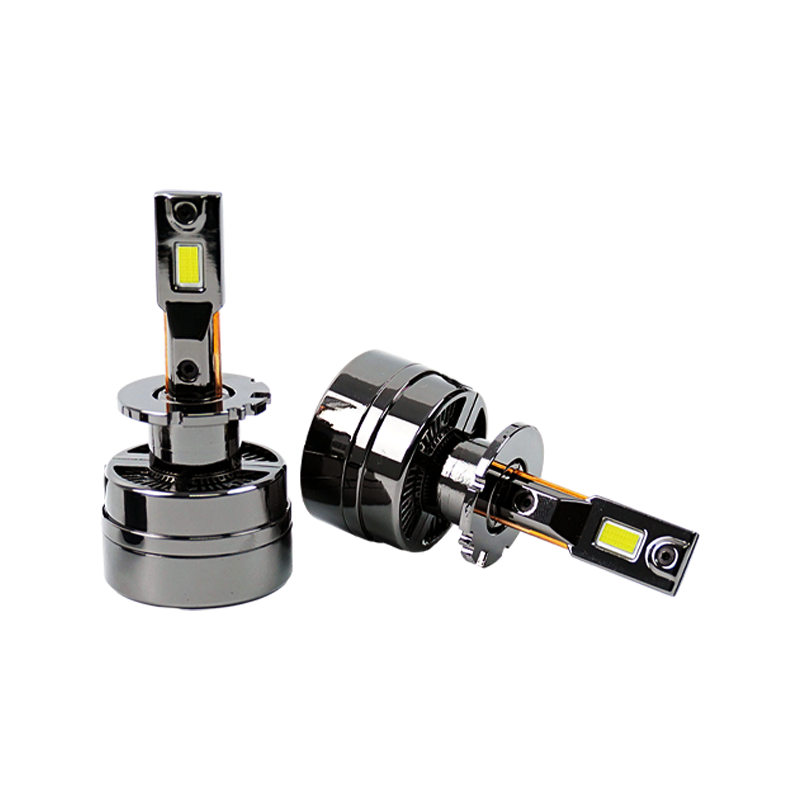
The number one motive of the radiator is to offer efficient warmness transfer and dissipation. LED headlight bulbs normally feature a small semiconductor chip that emits light while an electric current passes via it. As the chip illuminates, it generates heat. The radiator's number one task is to soak up this warmness from the chip and switch it to the encircling air, preventing a buildup of heat that might doubtlessly damage the LED.
Radiators for LED headlight bulbs are typically product of remarkable aluminum or copper that own exquisite thermal conductivity. These metals successfully take in the heat from the LED chip and transfer it to the encompassing fins or different heat-dissipating surfaces. The expanded surface place of the fins aids in dissipating the warmth into the air, ensuring a steady and safe temperature for the LED.
Furthermore, LED headlight bulbs frequently perform in enclosed areas within a car's headlight housing. Since these spaces can restrict right airflow, the radiator performs a crucial role in overcoming this problem. By efficaciously dissipating the heat generated, the radiator prevents the headlight bulbs from overheating and potentially causing damage no longer simply to the LEDs themselves, but also to the encircling components.
In summary, the presence of a radiator in LED headlight bulbs is important for efficient heat dissipation, permitting the LEDs to maintain their most appropriate overall performance and lifespan. The radiator absorbs the extra heat generated by using the LEDs and transfers it to the surrounding surroundings, stopping overheating and capacity harm. As LED era keeps to advance, radiator designs are also evolving to enhance warmth management and beautify the overall performance of LED headlight bulbs.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى русский
русский